NASA Rotor 37
This page contains various informations associated to one of the rotor 37 blade model used in LAVA publications.
Original model
- Original technical report [1]:
@TechReport{reid1978design, author = {Reid, L. and Moore, R. D.}, title = {Design and overall performance of four highly loaded, high speed inlet stages for an advanced high-pressure-ratio core compressor}, institution = {NASA Lewis Research Center Cleveland, OH, United States}, note = {NASA-TP-1337, url~: \url{https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19780025165}, 1978 (accessed 2020-10-29)}} - Pictures :
@Misc{huebler1977records, author = {Huebler, D.}, title = {Rotor 37 and stator 37 assembly. {R}ecords of the {N}ational {A}eronautics and {S}pace {A}dministration, 1903 - 2006. {P}hotographs relating to agency activities, facilities and personnel, 1973 - 2013}, note = {\href{https://catalog.archives.gov/id/17468361}{https://catalog.archives.gov/id/17468361}, 1977 (accessed 2020-10-29)}, % for Fig. 1 note = {\href{https://catalog.archives.gov/id/17468389}{https://catalog.archives.gov/id/17468389}, 1977 (accessed 2020-10-29)}, % for Fig. 2}
Finite element mesh
- Number of nodes: 5745
- Total number of elements: 1800
- Number of degrees of freedom: 16524
- Element type: quadratic pentahedron
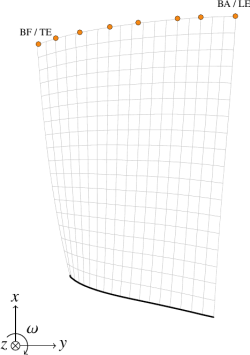
finite element mesh overview (coarse mesh)
- Number of nodes: 20657
- Total number of elements: 6664
- Number of degrees of freedom: 60588
- Element type: quadratic pentahedron
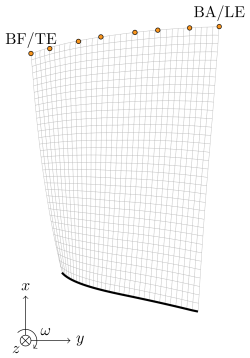
finite element mesh overview (refined mesh) - LaTeX source files
Material properties
- Rotor 37 is made of a 200-grade maraging steel [1]
-
- Young's modulus E = 180 GPa
- density$\rho$ = 8000 kg/m3
- Poisson's ratio $\nu$ = 0.3
- yield stress $\sigma_Y$ = 1.38 GPa (200 000 psi)
- First three predicted natural frequencies (with clamped root) for the coarse mesh:
- 1B: 5272.3 rad/s / 839.1 Hz
- 1T: 15760.5 rad/s / 2508.4 Hz
- 2B: 19071.3 rad/s / 3035.3 Hz
- First three predicted natural frequencies (with clamped root) for the refined mesh:
- 1B: 5368.7 rad/s / 838.5 Hz
- 1T: 15754.7 rad/s / 2507.4 Hz
- 2B: 19032.9 rad/s / 3029.2 Hz
Featured articles from the LAVA
Cette page contient diverses informations associées à l'un des modèles de l'aube NASA rotor 37 utilisé dans les publications du LAVA.
Modèle original
- Rapport technique original [1]:
@TechReport{reid1978design, author = {Reid, L. and Moore, R. D.}, title = {Design and overall performance of four highly loaded, high speed inlet stages for an advanced high-pressure-ratio core compressor}, institution = {NASA Lewis Research Center Cleveland, OH, United States}, note = {NASA-TP-1337, url~: \url{https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19780025165}, 1978 (accessed 2020-10-29)}} - Photographies :
@Misc{huebler1977records, author = {Huebler, D.}, title = {Rotor 37 and stator 37 assembly. {R}ecords of the {N}ational {A}eronautics and {S}pace {A}dministration, 1903 - 2006. {P}hotographs relating to agency activities, facilities and personnel, 1973 - 2013}, note = {\href{https://catalog.archives.gov/id/17468361}{https://catalog.archives.gov/id/17468361}, 1977 (accessed 2020-10-29)}, % for Fig. 1 note = {\href{https://catalog.archives.gov/id/17468389}{https://catalog.archives.gov/id/17468389}, 1977 (accessed 2020-10-29)}, % for Fig. 2}
Maillage éléments finis
- Nombre de noeuds : 5745
- Nombre total d'éléments : 1800
- Nombre de degrés de liberté : 16524
- Type d'élément : pentaèdre quadratique

aperçu du maillage éléments finis (maillage grossier)
- Nombre de noeuds : 20657
- Nombre total d'éléments : 6664
- Nombre de degrés de liberté : 60588
- Type d'élément : pentaèdre quadratique

aperçu du maillage éléments finis (maillage fin) - sources LaTeX
Propriétés matériau
- Le matériau du rotor 37 est un alliage à base de nickel : un acier maraging de grade 200 [1]
-
- Module d'Young E = 180 GPa
- masse volumique $\rho$ = 8000 kg/m3
- coefficient de Poisson $\nu$ = 0,3
- limite élastique $\sigma_Y$ = 1,38 GPa (200 000 psi)
- Trois premiers modes prévus (noeuds de la base encastrés) pour le maillage grossier :
- 1F : 5272,3 rad/s / 839,1 Hz
- 1T : 15760,5 rad/s / 2508,4 Hz
- 2F : 19071,3 rad/s / 3035,3 Hz
- Trois premiers modes prévus (noeuds de la base encastrés) pour le maillage fin :
- 1F : 5268,7 rad/s / 838,5 Hz
- 1T : 15754,7 rad/s / 2507,4 Hz
- 2F : 19032,9 rad/s / 3029,2 Hz
Articles du laboratoire
1.
a,
b,
c,
d
Reid. «Design and overall performance of four highly loaded, high speed inlet stages for an advanced high-pressure-ratio core compressor » 1978. p64 pdf

