Cubic and bicubic spline interpolation in Python
This page contains the source codes associated to the HAL technical note for setting up and plotting cubic splines and bicubic parametric surfaces with various end conditions.
Abstract
Cubic and bicubic spline interpolations are widely used in a variety of domains. Nonetheless, there are limited resources available to help students or professionals who wish to implement these tools within a computer program. Be it for visualization purposes or for use within sophisticated algorithms, building a 2D or a 3D spline may not be a straightforward process. In this context, the present technical note provides a brief theoretical description of both splines and bicubic splines but also focuses on the practical implementation of both concepts with an emphasis on the various types of boundary conditions that may be used. In particular, different configurations featuring free end conditions, not-a-knot end conditions or particular tangent orientations to build both open and closed parametric curves and surfaces are detailed. Several source codes—written in Python 3.8—are provided with the intent to facilitate the reproduction of presented results. Proceed to the bottom of the page for an overview of practical examples.
2D cubic spline
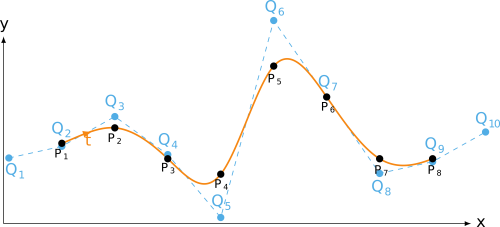
free end condition
Python source code: free end condition
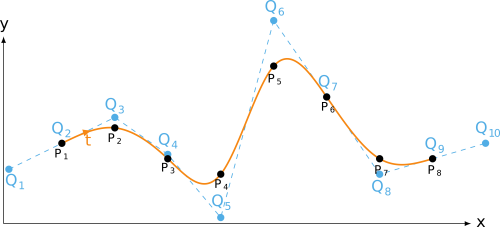
imposed tangent direction
Python source code: imposed tangent direction
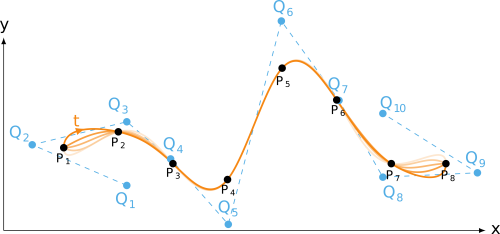
end-to-end tangent continuity
Python source code: end-to-end tangent continuity
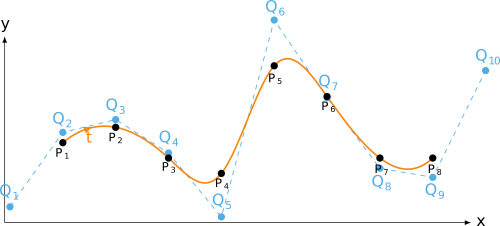
not-a-knot end condition
Python source code: not-a-knot end condition
3D bicubic parametric surface
free end condition
Python source code: free end condition
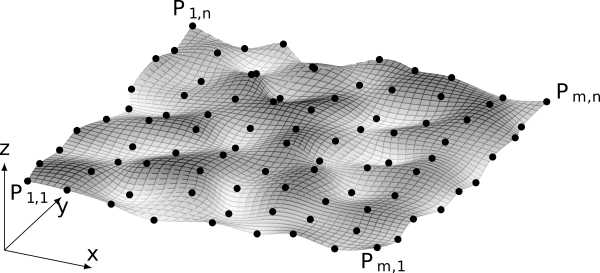
cylindrical closed surface
Python source code: cylindrical closed surface
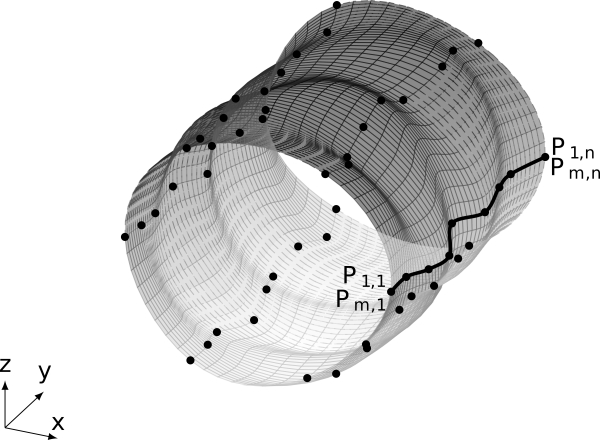
spherical closed surface
Python source code: spherical closed surface
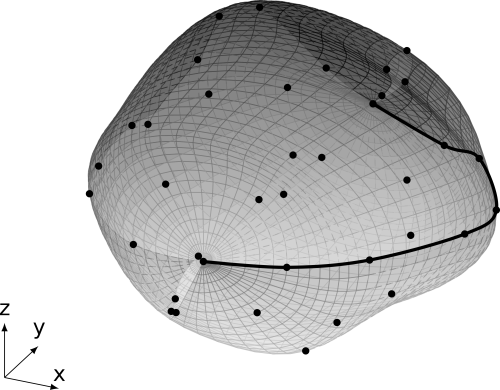
not-a-knot end condition
Python source code: not-a-knot end condition
